Inside Volume 1, Issue 2
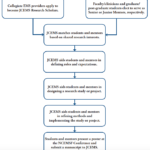
The JCEMS Research Mentorship Program
JCEMS developed a Research Mentorship Program to build research capacity in the collegiate EMS community.
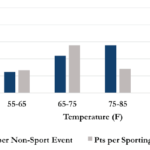
EMS Resource Utilization at College Campus Mass Gathering Events
This study aimed to examine EMS utilization during mass gathering events at an urban university with a collegiate-based EMS agency. Findings suggest that college event planners can potentially utilize event and weather features to predict EMS resource utilization.
Benzodiazepine & Alcohol Co-Ingestion
This clinical review discusses the relevant pharmacology, clinical presentation, and treatment of patients who have co-ingested benzodiazepines and alcohol.
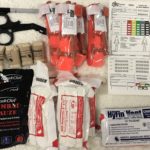
Implementation of Stop the Bleed on an Undergraduate College Campus
Johns Hopkins Emergency Response Organization (HERO) implemented a training, preparedness, and public access equipment program to stop the bleed on their campus.
Interview with Oren Cohn
JCEMS Executive Editor Brittany J. Dingler offers an exclusive interview with the 2018 Collegiate EMS Provider of the Year.
Inside Supplemental – 2018 Academic Poster Session
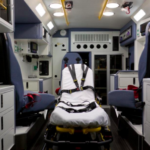
Designing Safety into Ambulances
Massachusetts Institute of Technology EMS designed an innovative new ambulance, incorporating best practices and current evidence to enhance provider safety.
Utilizing a Scramble Crew Approach to Achieve 24-Hour Coverage
In 2016, Muhlenberg College EMS reinstituted daytime response, incorporating Active 911, a digital messaging system, and an all-call, scramble crew model. Since the new response plan began in March of 2016, Muhlenberg College EMS has responded to 47 calls that may have otherwise been ignored, at a response time shorter than that of normal duty crew responses.
Expanding Collegiate EMS Agencies
Expanding EMS agencies face many challenges pertaining to on-scene operations, administrative oversight, and sustainability. Yale EMS (YEMS) faced a $5000 budget deficit, inconsistent training of probationary members, and a high incidence of equipment deficiencies, delayed response times, and unsafe scene conditions. YEMS addressed these concerns using a three-pronged approach tackling Operations, Administration, and Sustainability challenges.
MCI Training Program
In 2010, the University of Pennsylvania Medical Emergency Response Team (MERT) initiated the Mass Casualty Incident (MCI) training program. To better prepare student-EMTs to respond and manage a disaster scene, MERT is implementing a tabletop exercise module to ensure that MERT members are fluent in the Incident Command System (ICS), familiar with the MERT MCI operating guidelines, and able to size-up a scene appropriately.
“Continuing Care” with EC-ERT
EC-ERT created a program called “Continued Care” (CC) to provide a prehospital care resource for patients who required additional time to monitor their condition until care could be terminated. Through its design and implementation, CC reduces non-emergent ALS transports, thus reducing strain on the county EMS system and local emergencies rooms.
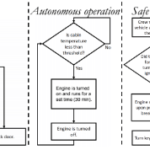
A Low-Cost Ambulance Idle Reduction System
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) EMS proposes a simple, automated system design that constantly monitors the temperature in the patient compartment, and only starts the vehicle engine and heating system temporarily when the temperature falls below a preset threshold in the cabin. MIT EMS estimates that their system can reduce the vehicle’s idling fuel consumption and engine run time by about 85%.
Implementing Stop the Bleed at Skidmore College
Skidmore College Emergency Medical Services (SCEMS) implemented a Stop to Bleed campaign at Skidmore College. SCEMS organized 20 free bleeding control trainings to train over 60 community members and incorporated $5,000 into the Skidmore Campus Safety 2018 budget for bleeding control equipment.
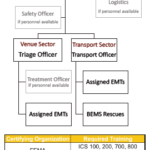
Optimizing Collegiate EMS Resources During Major Events
Brown EMS (BEMS) provides primary medical coverage at Spring Weekend (SWE), an annual outdoor concert drawing 6,000 attendees per day. By increasing its resources to include ground details and an additional ALS ambulance, BEMS aims to increase venue capacity, optimize response, and limit mutual-aid requirements.
Cardiac Health and Stroke Awareness Month (CHASAM)
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) EMS designed a non-certification learning opportunity for students who have not previously sought out CPR training. MIT EMS’s creation of an annual Cardiac Health and Stroke Awareness Month (CHASAM), piloted in 2016 and repeated in 2017, substantially increased the number of trained bystanders from a diverse selection of residential communities.
Feasibility of Asynchronous Learning in Collegiate EMS
Brown University EMS implemented a novel BLS Supervisor Training Program. Using asynchronous learning, Brown sought to optimize training time by promoting self-learning off-shift and outside of traditional didactic models using small-group, problem-based learning and online modules.
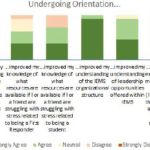
Piloting an Online New Member Orientation Program
Illini EMS created and implemented an online Orientation course for new members. Using a combination of original and adapted videos followed by a quiz, this self-paced program teaches and assesses the basics of topics including bleeding control, organizational structure, team dynamics, and First Responder mental health in under an hour.
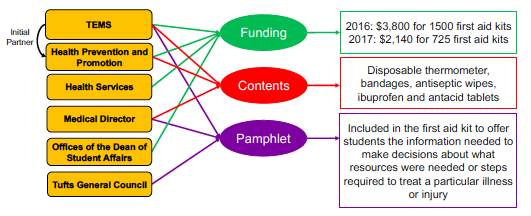
Upstream of EMS Overutilization
Tufts Emergency Medical Services—alongside Tufts Health Promotion and Prevention—funded, created, and distributed first aid kits and informational content to all first-year students.